The Significance of the T2-T4 Spine in Health and Wellness
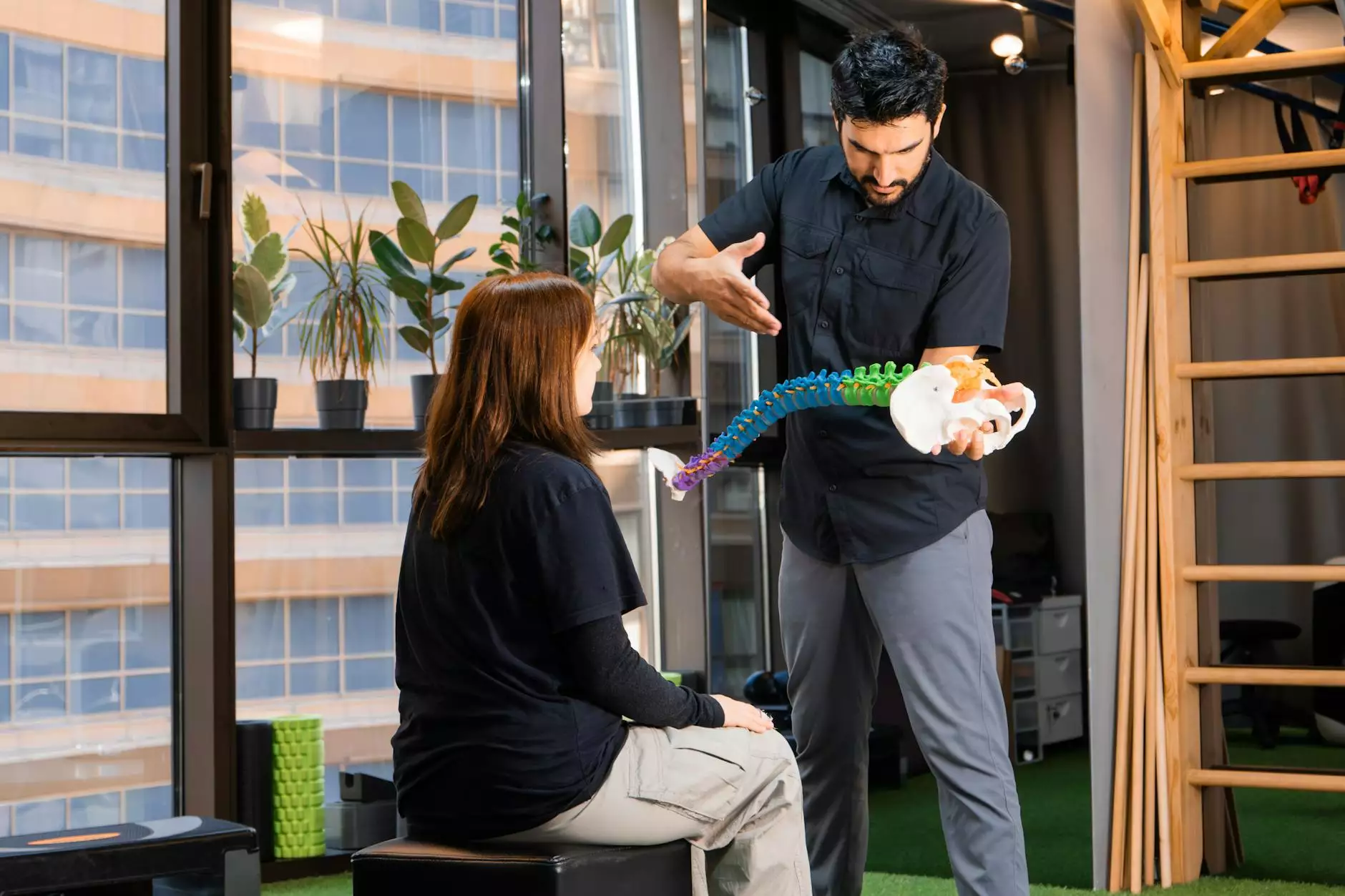

The human body is a complex and harmonious system, and the spine plays a critical role in maintaining our overall well-being. Of particular interest to healthcare professionals and those seeking therapeutic care is the T2-T4 spine, which consists of the second, third, and fourth thoracic vertebrae. Understanding its anatomy, function, and significance is essential for anyone interested in health, particularly in the fields of chiropractic care, physical therapy, and general wellness.
Understanding the Anatomy of the T2-T4 Spine
The thoracic spine comprises twelve vertebrae, labeled T1 through T12. The segments from T2 to T4 are located in the upper to middle section of the thoracic region. These vertebrae are characterized by their unique structural properties, which play specific roles in supporting the rib cage, protecting the spinal cord, and allowing for a range of motion. Here’s a closer look at each vertebra:
- T2 Vertebra: Positioned just below the first thoracic vertebra (T1), T2 serves as a connection point for the second rib and offers pivotal support to the upper thoracic region.
- T3 Vertebra: T3 corresponds to the level of the third rib. It is crucial for the alignment and stability of the spine, as well as for maintaining proper posture.
- T4 Vertebra: The fourth thoracic vertebra anchors the fourth rib and helps in the support of the thoracic organs, especially the heart and lungs, making it vital for respiratory health.
The Function of the T2-T4 Spine in the Human Body
The thoracic spine serves several crucial functions:
Protection of the Spinal Cord
The primary function of the entire vertebral column, including the T2-T4 spine, is to protect the spinal cord. The spinal cord is a vital part of the central nervous system (CNS) and is responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body. Any damage to the vertebrae can lead to severe neurological issues.
Support and Stability
The T2-T4 spine provides essential support to the upper body. This section of the spine helps keep the body upright, allowing for proper posture and alignment. A healthy thoracic spine is critical for athletes and anyone engaging in physical activities.
Facilitating Movement
The thoracic spine allows for various movements, including twisting and bending. While the lumbar spine (lower back) is more flexible, the thoracic spine's structure permits controlled motion that is necessary for many physical activities. The connections between vertebrae allow for the attachment of the ribs, enabling movements integral to breathing.
The Importance of Chiropractors in Maintaining a Healthy T2-T4 Spine
Chiropractors play a significant role in ensuring that the T2-T4 spine and the rest of the vertebral column are maintained in optimal condition. Here are several ways they assist in spinal health:
Assessment and Diagnosis
A chiropractor begins with a thorough assessment of the patient’s spine, focusing on the thoracic region. They use methods such as:
- Detailed medical history
- Physical examinations
- Diagnostic imaging (X-rays, MRI)
Spinal Adjustments
One of the cornerstone techniques in chiropractic care is spinal adjustments. This treatment can effectively realign misaligned vertebrae in the T2-T4 spine, improving overall function and reducing pain. Many patients report significant improvements in discomfort following these adjustments.
Rehabilitation Exercises
In addition to manual adjustments, chiropractors often recommend a regimen of rehabilitation exercises designed to strengthen the back and improve flexibility. These exercises help stabilize the thoracic spine and can enhance athletic performance.
Common Conditions Associated with the T2-T4 Spine
Various conditions can affect the T2-T4 spine, leading to discomfort and reduced mobility. Here are some common issues:
Thoracic Vertebral Fractures
Fractures in the thoracic vertebrae can result from trauma, such as accidents or falls. These injuries require immediate medical attention and often entail physical rehabilitation for recovery.
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
This condition occurs when the blood vessels or nerves become compressed in the area between the clavicle and the first rib. Symptoms may include pain, numbness, and weakness in the arms or hands.
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine. It often emerges during adolescence and can impact the thoracic spine, leading to changes in posture and potential complications for lung function.
Preventive Measures and Self-Care for a Healthy T2-T4 Spine
Taking proactive steps toward spinal health is essential. Here are some effective strategies for maintaining a healthy T2-T4 spine:
Maintain Proper Posture
Being mindful of your posture during daily activities is crucial. Whether sitting, standing, or lifting, maintaining good posture can alleviate unnecessary strain on the thoracic spine.
Engage in Regular Exercise
Incorporating strength training, flexibility exercises, and aerobic activities into your routine significantly benefits spinal health. Focus on core-strengthening exercises that support the back.
Use Ergonomic Furniture
Investing in ergonomic office furniture can reduce the risk of back strain, especially for individuals who spend prolonged hours seated at desks.
Conclusion
The T2-T4 spine is a pivotal component of the thoracic region, contributing to both mobility and stability. Understanding its anatomy and functions allows for better appreciation of its role in overall health.
Incorporating chiropractic care, along with preventive measures and self-care routines, can lead to optimal spinal health. Being proactive in maintaining a healthy T2-T4 spine not only enhances one's quality of life but also empowers individuals to pursue their passions with vigor and confidence.
Further Resources
For more information regarding the T2-T4 spine and chiropractic care, visit IAOM-US for expert guidance and support in your journey to health and wellness.